Calculate Strees-Strain of Circular Rod.
FEA of Circular Rod
An
external force operating across an object's cross-section is measured by
stress. N/m2 (SI) or lb/in2 are the units of force per area for stress (US).
Common names for the SI units are Pascals, abbreviated Pa. We frequently come
across 103 Pa = 1 kPa (kilo Pascal), 106 Pa = an MPa (mega Pascal), or 109 Pa =
GPa since the 1 Pa is uncomfortably little in comparison to the loads that most
constructions experience (Giga Pascal).

A building may encounter one of two
types of stress: Shear stress and regular stress. A force exerts normal stress
when it works perpendicular (or "normal") to an object's surface. A
force exerts a force on an object when it acts parallel to its surface.
.jpg)
Let's
suppose a case of Static Structure Analysis of circular bar under the tensile
load of 800KN. For this analysis, we will use Structural Steel having a Young's
Modulus of 240 GPA. The design was done on Solidworks software and for FEA
Ansys is used.
On
written calculation, we get the result as follows:
Change
in Length = 1.708 mm
Maximum
Stress Develop = 282.9MPa
Designing
was done on Solidworks by using the revolve command.
Boundary Condition:
.jpg) For
analysis, we have the method for setup
For
analysis, we have the method for setup
As we created the geometry and exported that in .igs format, our second step is to divide geometry into elements known as discretization. So for better results, we have to improve the mesh size. So in our case, we use the face mesh feature of 10 mm to get better results at critical or we can say the area in which we want to do a study.
Discretization of Circular Rod
After converting into elements the next step is
to apply the loading condition, for FEA we have to fix one side and apply load
on another side of this rod.

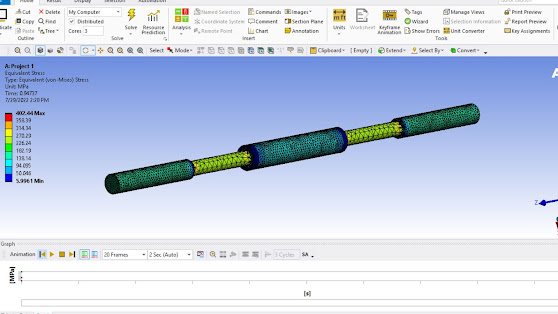
After
applying geometrical constrained the next step is to solve that and in
solutions, we analyze the Total Deformation and Equivalent Stress. Below the
result is attached.

- Total Deformation
.jpg)
- Equivalent Stress
.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment